Cleanroom Garments Required for ISO Class 5 Environments
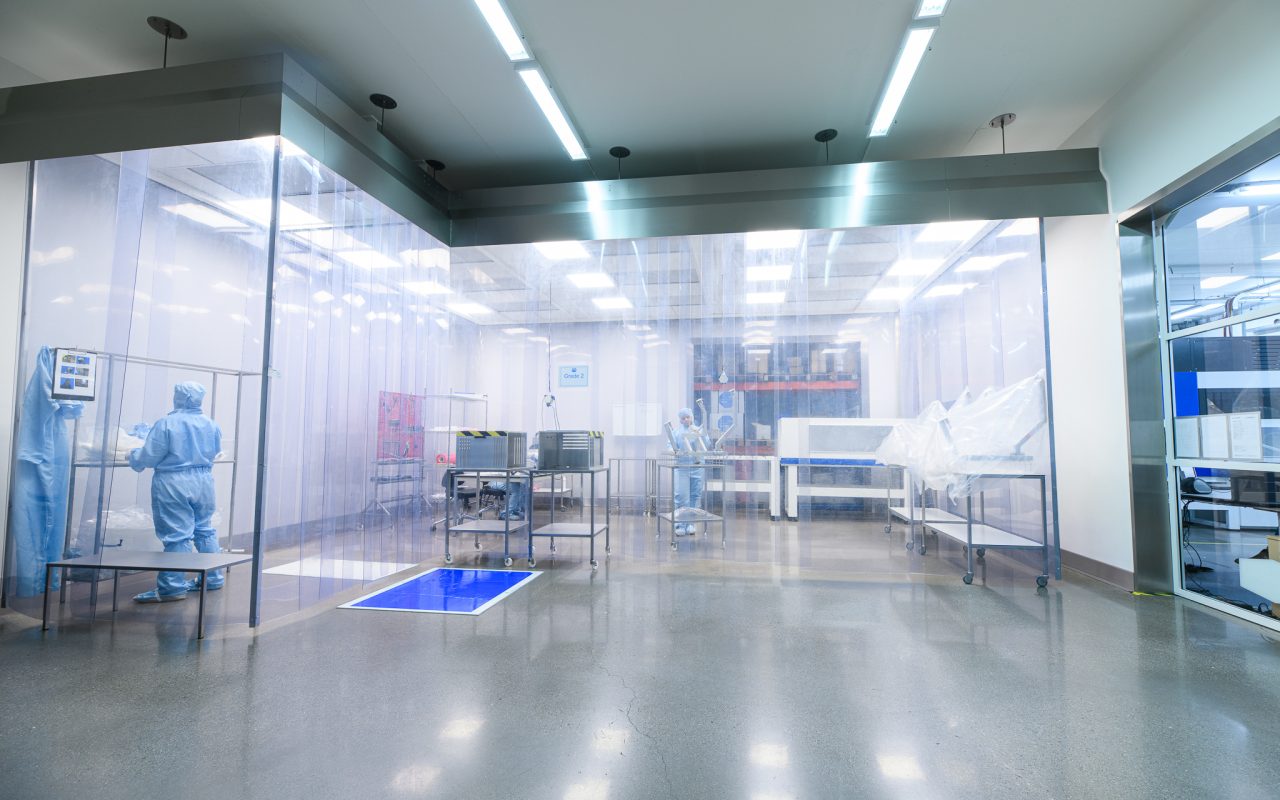

ISO Class 5 cleanrooms are controlled environments designed to maintain extremely low levels of airborne particles and microbial contamination. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, medical device manufacturing, and semiconductor production rely on these environments to ensure product quality and safety. One of the most critical factors in maintaining a cleanroom’s integrity is the use of proper garments, which prevent contaminants generated by personnel from compromising sensitive processes. Understanding the types of garments required and their proper use is essential for compliance and contamination control.
Personnel are a primary source of particles and microorganisms in cleanroom environments. Skin flakes, hair, respiratory droplets, and fibers from clothing can all contribute to contamination if not properly contained. Implementing an ISO Class 5 Cleanroom requires strict garment protocols to protect products and processes. These garments serve as a barrier between the operator and the controlled environment, minimizing the risk of introducing particles into the air or onto surfaces where sterile operations occur.
Types of Cleanroom Garments
The garments required in an ISO Class 5 environment are specifically designed to limit particle shedding and microbial contamination. The basic components of cleanroom apparel include coveralls or gowns, gloves, head covers, face masks, and footwear. Each component serves a specific function in preventing contamination.
Coveralls and Gowns
Coveralls or gowns are the primary barrier between the operator and the cleanroom environment. They are typically made from nonwoven synthetic materials such as polyester or polypropylene, which resist particle shedding. For ISO Class 5 environments, full-body coveralls that cover arms, legs, and torso are preferred. These garments often include elastic cuffs, sealed seams, and zipper closures to prevent particles from escaping.
Gowns are used in slightly less critical areas but still provide essential protection. Both coveralls and gowns must be laundered or sterilized according to cleanroom standards before use. Disposable or reusable options are available depending on the specific cleanroom protocols and contamination control requirements.
Gloves
Gloves are essential in ISO Class 5 cleanrooms to prevent contamination of products, surfaces, and equipment from hand contact. They are typically made from nitrile, latex, or neoprene materials. Gloves must fit properly to ensure dexterity and prevent tearing, which could compromise the barrier.
Gloves are often worn in multiple layers for highly sensitive processes. They should be changed frequently and sanitized as needed to prevent cross-contamination. Proper donning and removal techniques are critical to maintain cleanroom integrity.
Head Covers
Head covers, including hoods, bouffant caps, or full-face hoods, prevent hair, skin flakes, and respiratory particles from entering the controlled environment. In ISO Class 5 cleanrooms, full-coverage hoods that leave only the eyes exposed are commonly used in sterile pharmaceutical or biotechnology operations. The material must be non-shedding and compatible with sterilization protocols.
Face Masks and Respiratory Protection
Face masks reduce the release of respiratory droplets into the cleanroom environment. In ISO Class 5 settings, masks often cover both the nose and mouth and may include built-in eye protection in the form of visors. Some high-risk operations may require additional respiratory protection, such as powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), to maintain absolute sterility and prevent contamination from exhaled air.
Footwear and Boot Covers
Footwear contributes significantly to contamination if not properly controlled. ISO Class 5 cleanrooms require shoes or boots made from non-shedding, easily sanitized materials. Disposable boot covers are often used over regular cleanroom shoes to further reduce the risk of introducing particles from outside. Shoe covers are designed to be easy to don and remove without generating particles during the process.
Gowning Procedures and Protocols
Proper garment use in ISO Class 5 cleanrooms is as important as the garments themselves. Personnel must follow strict donning and doffing procedures to minimize particle generation. Typically, gowning is performed in a designated gowning area outside the cleanroom, following a step-by-step protocol that ensures each piece of apparel is worn correctly.
Training and adherence to these procedures are essential. Improper gowning, such as touching the exterior of gloves or garments, can compromise the barrier and introduce contaminants into critical areas. Regular refresher training ensures personnel maintain proper gowning habits over time.
Material Selection and Maintenance
Cleanroom garments are made from materials that are non-shedding, durable, and compatible with sterilization or laundering processes. Reusable garments must be laundered in certified cleanroom facilities to remove contaminants, while disposable garments are pre-sterilized and discarded after use. Material selection also considers comfort and breathability to enable personnel to work efficiently without compromising contamination control.
Importance in Contamination Control
The use of proper cleanroom garments is critical to maintaining the ISO Class 5 standard. Even a single human-generated particle can compromise sensitive pharmaceutical or biotechnology processes. By implementing appropriate apparel, training personnel, and following strict gowning protocols, organizations can significantly reduce contamination risks and maintain compliance with regulatory and quality standards.
In conclusion, garments play a pivotal role in protecting the integrity of ISO Class 5 cleanrooms. Coveralls, gloves, head covers, face masks, and footwear all serve as essential barriers against contamination. Proper gowning procedures, material selection, and maintenance ensure that these garments perform effectively, safeguarding sensitive processes and supporting compliance in highly controlled environments.