ISO 8 Cleanroom Validation and Certification Process
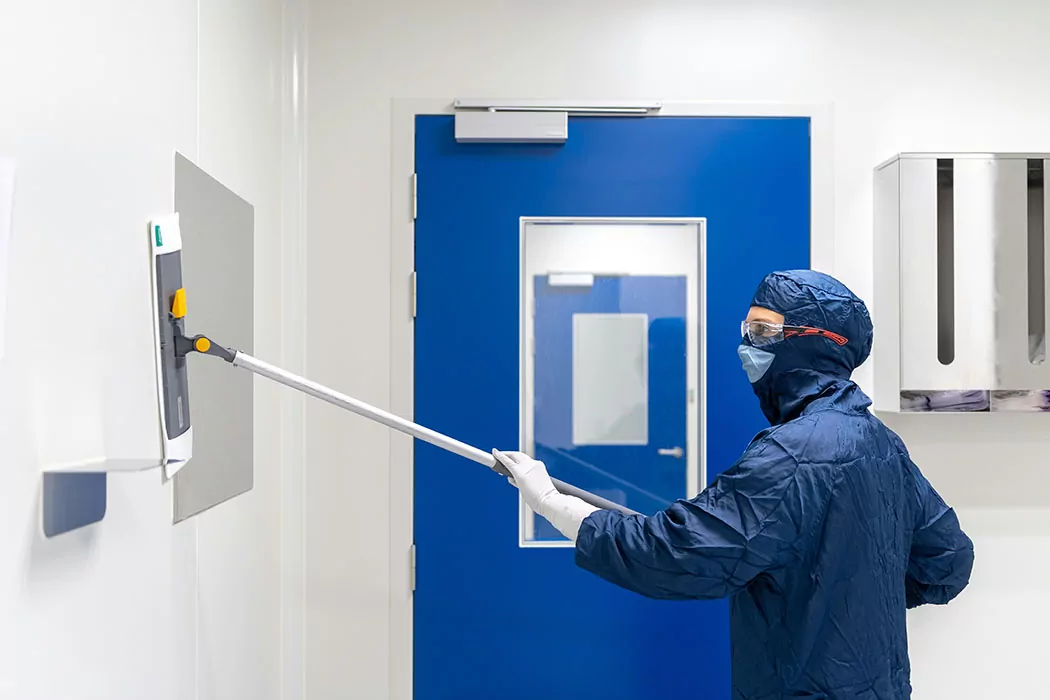

ISO 8 cleanrooms are controlled environments designed to maintain specific levels of airborne particulate contamination, temperature, humidity, and pressure to support non-critical manufacturing and laboratory processes. These cleanrooms are widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, biotechnology, and electronics, where contamination control is important but does not require the ultra-stringent conditions of ISO Class 5 or 7 cleanrooms. To ensure that an ISO 8 cleanroom operates effectively and meets industry standards, a rigorous validation and certification process is essential.
Validation and certification provide documented proof that the cleanroom meets the cleanliness, airflow, and environmental requirements defined by ISO 14644-1 standards. This process is critical not only for regulatory compliance but also for product safety, process reliability, and operational efficiency. For organizations seeking detailed guidance on cleanroom standards and best practices, resources such as the ISO 8 Cleanroom provide comprehensive information on validation, monitoring, and certification procedures.
Steps in ISO 8 Cleanroom Validation
The validation process for an ISO 8 cleanroom is conducted in multiple phases to confirm that the facility meets design specifications and maintains compliance during operation. Key steps include:
- Design Qualification (DQ): This phase ensures that the cleanroom design meets the required standards and specifications. Architects, engineers, and quality teams review the layout, airflow system, filtration, pressure differentials, and environmental control systems to verify that the cleanroom can achieve ISO 8 classification.
- Installation Qualification (IQ): During IQ, all components of the cleanroom, including HVAC systems, filters, sensors, and critical equipment, are inspected and tested to ensure they are installed according to manufacturer specifications and design requirements. IQ documentation includes equipment calibration, system specifications, and installation verification.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): OQ involves testing the cleanroom systems under controlled conditions to verify proper operation. This phase includes airflow velocity measurements, pressure differential tests, temperature and humidity monitoring, and filter integrity testing. OQ confirms that the cleanroom systems perform correctly across the expected operating range.
Performance Qualification (PQ)
Performance Qualification is the final stage in ISO 8 cleanroom validation. PQ evaluates the cleanroom under actual operational conditions to ensure that it consistently meets cleanliness and environmental standards. Key PQ activities include:
- Particle Count Testing: Airborne particle concentrations are measured using particle counters to confirm compliance with ISO 8 limits for various particle sizes. Testing is conducted at multiple points in the cleanroom, including critical work areas, to ensure uniform performance.
- Airflow and Pressure Testing: Air velocity and pressure differentials are measured under normal operating conditions. Positive pressure relative to surrounding areas is verified to prevent contamination ingress.
- Environmental Monitoring: Temperature and humidity are continuously monitored to ensure stability within specified tolerances. Monitoring equipment may also track fluctuations over extended periods to detect trends that could affect cleanroom performance.
Routine Monitoring and Revalidation
ISO 8 cleanroom validation does not end with initial certification. Routine monitoring is essential to maintain compliance and ensure long-term performance. Regular particle counting, airflow checks, pressure differential measurements, and environmental monitoring help identify deviations early. Any changes in processes, equipment, or layout require revalidation to ensure that the cleanroom continues to meet ISO standards.
Periodic requalification of critical systems, such as HEPA filters, HVAC components, and environmental control devices, is conducted according to standard operating procedures. Documentation of these activities supports regulatory compliance and demonstrates the ongoing reliability of the cleanroom.
Certification Process
Certification of an ISO 8 cleanroom is typically performed by independent third-party organizations or regulatory bodies. The certification process includes a comprehensive review of validation documentation, testing results, and operational procedures. Successful certification confirms that the cleanroom meets ISO 14644-1 requirements and is suitable for its intended use.
Certificates are usually valid for a specified period, after which recertification is required. Maintaining up-to-date certification is important for regulatory inspections, audits, and quality assurance programs. It also ensures confidence that products manufactured or tested within the cleanroom meet required contamination control standards.
Importance of Proper Validation and Certification
Proper validation and certification of ISO 8 cleanrooms offer several benefits. They provide assurance that environmental conditions meet industry standards, reduce the risk of contamination, and support consistent product quality. Validation also helps identify potential issues with airflow, filtration, or equipment before they affect operations. Furthermore, documented validation and certification are often required for regulatory compliance, customer confidence, and internal quality control audits.
Best Practices for Validation
To ensure effective ISO 8 cleanroom validation, organizations should follow several best practices:
- Develop a detailed validation plan outlining objectives, procedures, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Use calibrated and certified equipment for all testing activities.
- Train personnel in validation procedures, cleanroom operations, and contamination control protocols.
- Maintain comprehensive records of all validation, monitoring, and maintenance activities for traceability.
- Conduct periodic reviews and revalidation following changes in operations, equipment, or regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
ISO 8 cleanroom validation and certification are critical processes that ensure controlled environments meet the required cleanliness, airflow, and environmental standards. Through design, installation, operational, and performance qualifications, followed by routine monitoring and certification, organizations can maintain compliance, minimize contamination risks, and ensure consistent product quality. Proper validation and certification also provide regulatory assurance and support operational efficiency, making them essential components of effective cleanroom management.