How a Water pH Sensor Supports Compliance With Water Regulations

Ensuring water quality is a critical responsibility for municipal authorities, industrial facilities, and private water providers. Regulatory agencies worldwide establish strict guidelines to protect public health and the environment. One of the key parameters monitored in these regulations is pH, which measures the acidity or alkalinity of water. Maintaining pH within the required range helps prevent infrastructure damage, optimize water treatment processes, and safeguard human health.
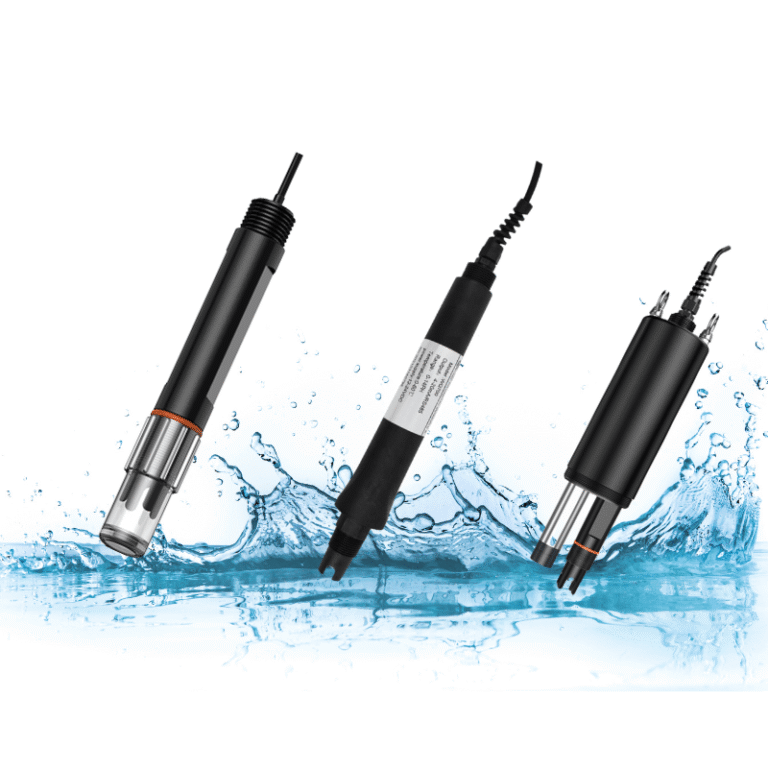
A reliable solution for monitoring pH and supporting regulatory compliance is a water ph sensor. By providing continuous, real-time measurements of water’s acidity or alkalinity, this device allows operators to maintain compliance with legal standards efficiently. Integrating such sensors into water management systems ensures timely detection of deviations and facilitates corrective actions before regulatory limits are exceeded.
The Role of pH in Water Regulations
pH is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 representing neutrality. Values below 7 indicate acidity, while values above 7 indicate alkalinity. Regulatory bodies typically require drinking water to maintain a pH range between 6.5 and 8.5. Water outside this range may become corrosive or scale-forming, potentially causing damage to pipes and treatment equipment, reducing disinfectant efficiency, and affecting taste and safety.
By continuously monitoring pH levels, water providers can ensure that their systems remain within regulatory limits. Accurate pH measurement is a fundamental aspect of water quality management and is often cited in compliance reports and audits.
How a Water pH Sensor Ensures Accurate Monitoring
Water pH sensors operate by detecting hydrogen ion concentration in water and converting this information into an electrical signal, which is then translated into a pH reading. Modern sensors are highly precise and designed for continuous operation, providing real-time data without the need for frequent manual testing.
With a water ph sensor, operators can track trends, identify sudden changes, and receive automated alerts if pH levels move outside acceptable ranges. This proactive monitoring approach enhances compliance by preventing violations before they occur and reducing the risk of penalties.
Protecting Public Health and Safety
Maintaining pH within regulated limits is essential for public health. Acidic water can corrode pipes and release toxic metals such as lead or copper into drinking water. Alkaline water may reduce the effectiveness of disinfectants, allowing harmful microorganisms to survive. Continuous pH monitoring with a water pH sensor ensures early detection of unsafe conditions, enabling corrective action to protect consumers.
Reliable monitoring also allows facilities to maintain consistent water quality, reducing health risks and supporting public trust in water systems.
Supporting Efficient Water Treatment
Water treatment processes, including disinfection and chemical dosing, are sensitive to pH levels. Disinfectants such as chlorine work most effectively within a specific pH range. Deviations can reduce chemical efficiency, requiring higher doses to achieve the desired results and increasing operational costs.
A water pH sensor provides continuous feedback, allowing operators to optimize chemical dosing and treatment protocols. By maintaining proper pH levels, water providers can ensure efficient treatment while minimizing waste and staying within regulatory standards.
Applications Across Sectors
While municipal drinking water systems are the primary users of pH sensors, they are also valuable in industrial, agricultural, and environmental applications. Industrial facilities monitor pH to comply with discharge regulations and protect equipment. Agricultural operations use pH sensors to maintain irrigation water quality and safeguard soil health. Environmental monitoring programs rely on pH data to detect pollution events and support regulatory reporting.
In all these applications, accurate pH measurement ensures adherence to legal requirements and promotes sustainable water management practices.
Improving Documentation and Reporting
Regulatory compliance often requires detailed records of water quality, including pH measurements. Water pH sensors facilitate this by automatically logging continuous data, which can be stored for reporting, audits, and inspections. This reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual testing and ensures transparency in regulatory submissions.
Automated monitoring also supports long-term trend analysis, helping organizations demonstrate consistent adherence to standards and implement improvements based on reliable data.
Conclusion
Maintaining compliance with water regulations is essential for protecting public health, safeguarding infrastructure, and ensuring efficient water treatment. A water pH sensor provides continuous, accurate monitoring of pH levels, enabling early detection of deviations, optimized treatment processes, and comprehensive documentation for audits and reporting. By integrating these sensors into water management systems, operators can ensure safe, reliable, and legally compliant water for municipal, industrial, and environmental applications.