Why Cold Die Forging Is Ideal for Producing High-Strength Metal Components
In modern manufacturing, producing metal components that offer both high strength and precision is essential across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Cold Die Forging has emerged as a reliable method for achieving these requirements by shaping metal at room temperature using high-pressure dies. This technique enhances mechanical properties while providing excellent dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for critical applications.
Using Cold Die Forging allows manufacturers to produce metal parts that are stronger and more reliable than those made with traditional casting or machining methods. By applying controlled pressure to deform metal at ambient temperatures, this process refines the internal grain structure, resulting in components that can withstand heavy loads, stress, and fatigue.
The Cold Die Forging Process
1. Material Selection
The process begins with selecting suitable metal or alloy, commonly steel, aluminum, or copper. The choice depends on the required mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and intended application.
2. Preparation of Workpieces
Unlike hot forging, cold die forging does not require heating the metal. The workpieces are cleaned and cut to the appropriate size before being placed in the forging die. The absence of heat reduces energy consumption and improves dimensional stability.
3. Die Design and Setup
Precision-machined dies determine the final shape of the component. The dies are designed to optimize material flow, minimize flash, and achieve the desired geometry with tight tolerances. Proper die design is crucial for producing accurate and repeatable parts.
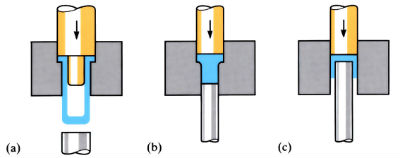
4. Forging Operation
The metal workpiece is placed in the die cavity, and high pressure is applied to force it into the shape of the die. This controlled deformation aligns the internal grains of the metal along the contours of the part, enhancing strength, durability, and fatigue resistance.
5. Flash Removal and Finishing
Excess material, or flash, is trimmed, and the part undergoes finishing processes such as machining, polishing, or heat treatment if required. These steps ensure the component meets dimensional specifications and surface quality standards.
Benefits of Cold Die Forging
High Strength and Durability
Cold die forging improves the mechanical properties of metal components by refining the internal grain structure. This results in parts with enhanced tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and impact toughness, making them suitable for high-stress applications.
Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy
Because the process occurs at room temperature, components experience minimal thermal expansion or contraction, allowing for tight tolerances and precise dimensions. This reduces the need for extensive post-forging machining.
Superior Surface Finish
Cold forging produces smooth surfaces with minimal defects, reducing the need for additional finishing processes. This not only saves time but also enhances the appearance and performance of the component.
Material Efficiency
The process is highly efficient, producing components with minimal waste. The controlled metal flow and precise die design minimize excess material, making cold die forging cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Faster Production Cycles
Cold die forging allows for rapid production of high-quality components, making it suitable for mass production. Once dies are prepared, large volumes of identical parts can be manufactured efficiently, reducing lead times.
Versatility in Applications
This forging method accommodates complex shapes, small components, and high-precision parts. It is particularly valuable for automotive components like gears, shafts, and fasteners, as well as aerospace structural parts and industrial machinery components.
Applications Across Industries
- Automotive: Gears, shafts, fasteners, and suspension components.
- Aerospace: Structural components, brackets, and high-strength connectors.
- Industrial Machinery: Couplings, hydraulic parts, and mechanical linkages.
- Consumer Goods: Durable components for appliances, tools, and electronics.
Conclusion
Cold Die Forging is an ideal manufacturing method for producing high-strength, precise, and durable metal components. Its ability to enhance mechanical properties, maintain tight tolerances, and support efficient mass production makes it invaluable for industries with demanding performance standards.
For manufacturers seeking reliable, high-quality parts that combine strength and accuracy, cold die forging offers a versatile and cost-effective solution that meets the rigorous demands of modern industrial applications.